Microsoft Patch Release Schedule
Patch Tuesday (also known as Update Tuesday[1]) is an unofficial term used to refer to when Microsoft regularly releases software patches for its software products. It is widely referred to in this way by the industry.[2][3][4] Microsoft formalized Patch Tuesday in October 2003.[5]
- Microsoft Patch Release Schedule 2017
- Microsoft Patch Release Schedule Pdf
- Microsoft Patch Release Notification
- Microsoft Patch Release Schedule 2016
- Microsoft Patch Release Schedule 1
- When Does Microsoft Release Patches
Patch Tuesday. Microsoft formalized Patch Tuesday in October 2003. Patch Tuesday occurs on the second, and sometimes fourth, Tuesday of each month in North America. As far as the integrated Windows Update (WU) function is concerned, Patch Tuesday begins at 18:00 or 17:00 UTC (10:00 PST (UTC−8) or 10:00 PDT (UTC−7)). On November 13, 2018, we re-released the Windows 10 October Update (version 1809), Windows Server 2019, and Windows Server, version 1809. We encourage you to wait until the feature update is offered to your device automatically. A summary of the current status of the October Update can be found below.
Patch Tuesday occurs on the second, and sometimes fourth, Tuesday of each month in North America. As far as the integrated Windows Update (WU) function is concerned, Patch Tuesday begins at 18:00 or 17:00 UTC (10:00 PST (UTC−8) or 10:00 PDT (UTC−7)).[6] The updates show up in Download Center before they are added to WU, and the KB articles and the Technet bulletin are unlocked later.
Microsoft has a pattern of releasing a larger number of updates in even-numbered months, and fewer in odd-numbered months.[7][8][9] Minor updates are also released outside Patch Tuesday. Daily updates consist of malware database refreshes for Windows Defender and Microsoft Security Essentials. Sometimes there is an extraordinary Patch Tuesday, two weeks after the regular Patch Tuesday. Some updates could be released at any time.[10]
- 3Exploit Wednesday
History[edit]
Starting with Windows 98, Microsoft included Windows Update that once installed and executed, would check for patches to Windows and its components, which Microsoft would release intermittently. With the release of Microsoft Update, this system also checks for updates for other Microsoft products, such as Microsoft Office, Visual Studio and SQL Server.
Microsoft Patch Release Schedule 2017
Earlier versions of Windows Update suffered from two problems:
- Less-experienced users often remained unaware of Windows Update and did not install it. Microsoft countered this issue, in Windows ME with the Automatic Updates component, which displayed availability of updates, with the option of automatic installation.
- Customers with multiple copies of Windows, such as corporate users, not only had to update every Windows deployment in the company but also to uninstall patches issued by Microsoft that broke existing functionality.
Microsoft introduced 'Patch Tuesday' in October 2003 to reduce the cost of distributing patches.[11] This system accumulates security patches over a month, and dispatches them all on the second Tuesday of each month, an event for which system administrators may prepare. The following day, informally known as 'Exploit Wednesday',[12] marks the time when exploits may appear in the wild which take advantage on unpatched machines of the newly announced vulnerabilities.
Tuesday was chosen as the optimal day of the week to distribute software patches. This is done to maximize the amount of time available before the upcoming weekend to correct any issues that might arise with those patches, while leaving Monday free to address other unanticipated issues that might have arisen over the preceding weekend[citation needed].
Security implications[edit]
An obvious security implication is that security problems that have a solution are withheld from the public for up to a month. This policy is adequate when the vulnerability is not widely known or is extremely obscure, but that is not always the case.
There have been cases where vulnerability information became public or actual worms were circulating prior to the next scheduled Patch Tuesday. In critical cases Microsoft issues corresponding patches as they become ready, alleviating the risk if updates are checked for and installed frequently.
At the Ignite 2015 event, Microsoft revealed a change in distributing security patches. They release security updates to home PCs, tablets and phones as soon as they are ready, while enterprise customers will stay on the monthly update cycle, which was reworked as Windows Update for Business.[13]
Exploit Wednesday[edit]
Many exploitation events are seen shortly after the release of a patch;[14]analysis of the patch helps exploit developers to immediately take advantage of the previously undisclosed vulnerability, which will remain in unpatched systems.[15] Therefore, the term 'Exploit Wednesday' was coined.[16]
Discontinued Windows versions[edit]
Microsoft warned users that it discontinued support for Windows XP starting on April 8, 2014 – users running Windows XP afterwards would be at the risk of attacks. As security patches of newer Windows versions can reveal similar (or same) vulnerabilities present in both newer and older Windows versions, this can allow attacks on devices with unsupported Windows versions (c.f. 'zero-day attacks'). However Microsoft stopped fixing such (and other) vulnerabilities in unsupported Windows versions, regardless how widely known such vulnerabilities became, leaving these vulnerabilities unfixed and devices running these Windows versions vulnerable to attacks. Microsoft made a singular exception during the rapid spread of the WannaCry ransomware and released patches in May 2017 for the by then unsupported Windows XP, Windows 8, and Windows Server 2003 (in addition to then supported Windows versions).[17]
Microsoft Patch Release Schedule Pdf
For Windows Vista 'extended support' was ended April 11, 2017, which will leave vulnerabilities discovered afterwards unfixed, creating the same situation for Vista as for XP before.[18]
For Windows 7 (with Service Pack 1; support has already run out without it) support will end January 14, 2020,[18] and on January 10, 2023 for Windows 8.1;[18] this will cause the same 'unfixed vulnerabilities' issue for users of these operating systems. Support for Windows 8 already ended January 12, 2016 (with users having to install Windows 8.1 or Windows 10 to continue to get support), and support for Windows 7 without SP1 was ended April 9, 2013 (with the ability to install SP1 to continue to get support until 2020, or having to install Windows 8.1 or Windows 10 to receive support after 2020).[18]
Windows 10[edit]
One major change with the introduction of Windows 10 was that Microsoft started to release a new version of Windows 10 twice per year, and with Microsoft's 'modern lifecycle policy' a newly released Windows 10 version starts a 'grace period' for the previous version with regard to support – unlike previous Windows products which received only infrequent updates via service packs, and support was governed by the 'fixed lifecycle policy'. With this new policy Home and Pro versions of Windows 10 will be provided with security and feature updates (so called 'mainstream support') for up to 18 months after release, 'enterprise' and education versions for 24 months.[18] To give an example: support for Windows 10 Home/Pro version 1703 (which was released in April 2017) will be stopped by Microsoft in October 2018, and support for versions 1507 and 1511 (released in 2015) officially ended in 2017.[19] Microsoft announced that it would give 'extended support' (security but not feature updates) for at least one 'semi-annual channel' (SAC) Windows 10 version until October 14, 2025.[20]
According to Microsoft a 'device needs to install the latest version (feature update) before [the] current version reaches end of service to help keep your device secure and have it remain supported by Microsoft'.[18] As with previous Windows operating systems, any device running such an unsupported version of Windows (which no longer receives security patches) is potentially affected by the 'unfixed vulnerabilities' issue beginning with the 'end of support' date. To counter this Microsoft has designed the update system for the Home and Pro editions of Windows 10 so that in most cases if technically possible the latest Windows version is downloaded and installed automatically – this has however drawn criticism due to other problems such forced upgrades can introduce.
<>Old version, no longer supported:April 9, 2019[21]| Current Windows 10 versions | ||||||||
| Version | Codename | Build | Marketing name | Release date | Support until (and support status by color) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTSC | Mobile | ||||||
| 1507 | Threshold 1 | 10240 | N/A | July 29, 2015 | Old version, no longer supported: May 9, 2017 | Older version, yet still supported: October 14, 2025 | N/A | |
| 1511 | Threshold 2 | 10586 | November Update | November 10, 2015 | Old version, no longer supported: October 10, 2017 | N/A | Old version, no longer supported: January 9, 2018 | |
| 1607 | Redstone 1 | 14393 | Anniversary Update | August 2, 2016 | Older version, yet still supported: October 13, 2026 | Old version, no longer supported: October 9, 2018 | ||
| 1703 | Redstone 2 | 15063 | Creators Update | April 5, 2017 | Old version, no longer supported: October 9, 2018 | Older version, yet still supported: October 8, 2019 | N/A | Old version, no longer supported: June 11, 2019 |
| 1709 | Redstone 3 | 16299 | Fall Creators Update | October 17, 2017 | Old version, no longer supported: April 9, 2019 | Older version, yet still supported: April 14, 2020 | Current stable version:December 10, 2019 | |
| 1803 | Redstone 4 | 17134 | April 2018 Update | April 30, 2018 | Older version, yet still supported: November 12, 2019 | Older version, yet still supported: November 10, 2020 | N/A | |
| 1809 | Redstone 5 | 17763 | October 2018 Update | November 13, 2018 | Older version, yet still supported: May 12, 2020 | Older version, yet still supported: May 11, 2021 | Current stable version:January 9, 2029 | |
| 1903 | 19H1 | 18362 | May 2019 Update | May 21, 2019 | Current stable version:December 8, 2020 | N/A | ||
| 1909 | 19H2 | 18363 | N/A | Fall 2019 | Latest preview version of a future release: 18 months | Latest preview version of a future release: 30 months | ||
| TBA | 20H1 | 18995 | TBA | Latest preview version of a future release: 18 months | ||||
Old version Latest version Future release | ||||||||
In addition to the commonly used editions like Home and Pro, Microsoft offers specialized 'Long-Term Servicing Branch' (LTSB) or 'Long-Term Servicing Channel' (LTSC) versions of Windows 10 with longer support timelines, governed by Microsoft's 'fixed lifecycle policy', e.g. 'Windows 10 Enterprise 2016 LTSB' will receive extended support until October 13, 2026.[18]
Adoption by other companies[edit]
SAP's 'Security Patch Day', when the company advises users to install security updates, was chosen to coincide with Patch Tuesdays.[22]Adobe Systems' update schedule for Flash Player since November 2012 also coincides with Patch Tuesday.[23] One of the reasons for this is that Flash Player comes as part of Windows starting with Windows 8 and Flash Player updates for the built-in and the plugin based version both need to be published at the same time in order to prevent reverse-engineering threats.
Bandwidth impact[edit]
Windows Update uses the Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) to download the updates, using idle network bandwidth.[24] However BITS will use the speed as reported by the network interface (NIC) to calculate bandwidth. This can lead to bandwidth calculation errors, for example when a fast network adapter (e.g. 10 Mbit/s) is connected to the network via a slow link (e.g. 56 kbit/s) – according to Microsoft 'BITS will compete for the full bandwidth [of the NIC] .. BITS has no visibility of the network traffic beyond the client.'[25]
Furthermore the Windows Update servers of Microsoft do not honor the TCP's slow-start congestion control strategy.[26] As a result, other users on the same network may experience significantly slower connections from machines actively retrieving updates. This can be particularly noticeable in environments where many machines individually retrieve updates over a shared, bandwidth-constrained link such as those found in many multi-PC homes and small to medium-sized businesses. Bandwidth demands of patching large numbers of computers can be reduced significantly by deploying Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) to distribute the updates locally.
In addition to updates being downloaded from Microsoft servers, Windows 10 devices can 'share' updates in a peer-to-peer fashion with other Windows 10 devices on the local network, or even with Windows 10 devices on the internet. This can potentially distribute updates faster while reducing usage for networks with a metered connection.[27][28]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^'August updates for Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2'. Windows Experience Blog. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^'Microsoft Patch Tuesday to target Windows, IE'. CNet. October 10, 2011. Retrieved November 9, 2011.
- ^'.NET Framework 1.1 Servicing Releases on Windows Update for 64-bit Systems'. Microsoft. March 28, 2006. Archived from the original on March 27, 2012. Retrieved November 8, 2011.
- ^'Understanding Windows automatic updating'. Microsoft — Understanding Windows — Get Help. Retrieved July 3, 2014.
- ^Budd, Christopher. 'Ten Years of Patch Tuesdays: Why It's Time to Move On'. GeekWire. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- ^Trent, Rod (2004). The Administrator Shortcut Guide to Patch Management. p. 51. ISBN9781931491365.
- ^Gregg Keizer (9 June 2011). 'Microsoft slates hefty Patch Tuesday, to fix 34 flaws next week'. Computerworld. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^'Microsoft Ready To Patch 34 Security Vulnerabilities'. ITProPortal. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^Gregg Keizer. 'Microsoft to patch critical Windows Server vulnerability'. Techworld. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^'Patch Tuesday: WM 6.1 SMTP fix released!'. Microsoft — Outlook Mobile Team Blog. November 11, 2008. Retrieved November 9, 2011.
- ^'Microsoft details new security plan'. News.cnet.com. Retrieved 2013-02-12.
- ^Paul Oliveria (Trend Micro Technical Communications) (4 October 2006). 'Patch Tuesday… Exploit Wednesday'. Blog.trendmicro.com. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- ^'Windows 10 bombshell: Microsoft to KILL OFF Patch Tuesday'. theregister.co.uk. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^'Exploit Wednesday'. afterdawn.com. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^Kurtz, George (2010-01-14). 'Operation 'Aurora' Hit Google, Others'. mcafee.com. Archived from the original on 2012-01-17. Retrieved 2014-08-12.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- ^Leffall, Jabulani (2007-10-12). 'Are Patches Leading to Exploits?'. Redmond Magazine. Retrieved 2009-02-25.
- ^'Customer Guidance for WannaCrypt attacks'. MSRC. Retrieved 2017-11-23.
- ^ abcdefg'Windows lifecycle fact sheet'. Microsoft. 2015-08-31. Retrieved 2015-08-31.
- ^'Windows 10 v1507 End of Servicing for CB and CBB'. support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2019-08-04.
- ^'Search product life cycle – Windows 10'. support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2019-08-04.
- ^ ab'Microsoft agrees to extend support deadline for Clover Trail PCs (till 2023)'. zdnet.com. 2017-07-19. Retrieved 2019-08-17.
- ^von Etizen, Chris (2010-09-15). 'SAP introduces a patch day'. The H Security. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ^McAllister, Neil (2012-11-08). 'Adobe switches Flash fix schedule to Patch Tuesdays'. The Register. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ^'About BITS'. MSDN. Microsoft. Retrieved 26 March 2016.
- ^MSDN BITS Network Bandwidth
- ^Strong, Ben (2010-11-25). 'Google and Microsoft Cheat on Slow Start'. benstrong.com. Archived from the original(blog) on December 7, 2013.
- ^Warren, Tom (15 March 2015). 'Microsoft to deliver Windows 10 updates using peer-to-peer technology'. The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^Chacos, Brad (3 August 2015). 'How to stop Windows 10 from using your PC's bandwidth to update strangers' systems'. PC World. IDG.
Further reading[edit]
- Evers, Joris (2005-09-09). 'Microsoft pulls 'critical' Windows update'. CNET News.com. Retrieved 2006-12-12.
- Schneier, Bruce (17 July 2006). 'Zero-Day Microsoft PowerPoint Vulnerability'. Schneier on Security. Example of report about vulnerability found in the wild with timing seemingly coordinated with 'Patch Tuesday'
- Schneier, Bruce (7 September 2006). 'Microsoft and FairUse4WM'. Schneier on Security. Example of a quick patch response, not due to a security issue but for DRM-related reasons.
External links[edit]
Patch Tuesday is the name given to the day each month that Microsoft releases security and other patches for their operating systems and other software.
Patch Tuesday is always the second Tuesday of each month and more recently is being referred to as Update Tuesday.
Microsoft Patch Release Notification
Non-security updates to Microsoft Office tend to occur on the first Tuesday of each month and firmware updates for Microsoft's Surface devices on the third Tuesday of every month.
Microsoft Patch Release Schedule 2016
Most Windows users will experience more of a Patch Wednesday because they're prompted to install, or notice the installation of, the updates downloaded via Windows Update on Tuesday night or Wednesday morning.
Some half-jokingly refer to the day after Patch Tuesday as Crash Wednesday, referring to the troubles that sometimes accompany a computer after the patches are installed (honestly, this rarely happens).
Latest Patch Tuesday: April 9, 2019
The latest Patch Tuesday was on April 9, 2019 and consisted of 34 individual security updates, correcting 75 unique issues across Microsoft Windows operating systems and some other Microsoft software.
Sep 05, 2017 Windows 10 LTSB clients and Windows Server 2016-based computers can still install the.NET Framework 4.7 from the Microsoft Download Center. On the Microsoft Update Catalog, we have also provided new.NET Framework 4.7 Windows Update bundles specifically for LTSB computers to let enterprises import the updates. Dot net framework download for windows 10. Nov 20, 2007 Important: Make sure you have the latest service pack and critical updates for the version of Windows on the computer. To look for recent updates, visit Windows Update. In addition, make sure you have Windows Installer 3.1 installed before you install this service pack; Click the Download button on this page to start the download; To save the download to your computer for installation at a. Downloads for.NET Framework and.NET Core, including ASP.NET and ASP.NET Core. Not sure where to start? See the Hello World in 10 minutes tutorial to install.NET and build your first app.NET is open-source and cross-platform, with free development tools for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Oct 09, 2012 Note: Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 include the.NET Framework 4.5. Therefore, you don't have to install this software on those operating systems. On this page, choose the Download button. To install the software now, choose the Run button.
The next Patch Tuesday will be on May 14, 2019.
Microsoft Patch Release Schedule 1
If you're currently using Windows 8.1 but have not yet applied the Windows 8.1 Update package or updated to Windows 10, you must do so to continue to receive these important security patches! See our Windows 8.1 Update piece for more on what this is and how to upgrade or How to Download Windows 10 for more on that upgrade.
When Does Microsoft Release Patches
What Do These Patch Tuesday Updates Do?
These patches from Microsoft update several individual files involved in making Windows and other Microsoft software work.
These files were determined by Microsoft to have security issues, meaning that they have 'bugs' that could provide a means to do something malicious to your computer without your knowledge.

How Do I Know If I Need These Security Updates?
You need these updates if you're running any supported edition of Microsoft's operating systems, 32-bit or 64-bit. This includes Windows 10, Windows 8 (as well as Windows 8.1), and Windows 7, plus supported Server versions of Windows.
A number of other products are receiving patches this month too. You can see the full list on Microsoft's Security Update Guide page, along with the associated KB articles and security vulnerability details. Just set the date filter from 4/9/2019 to 4/9/2019 to avoid showing previous months' updates.
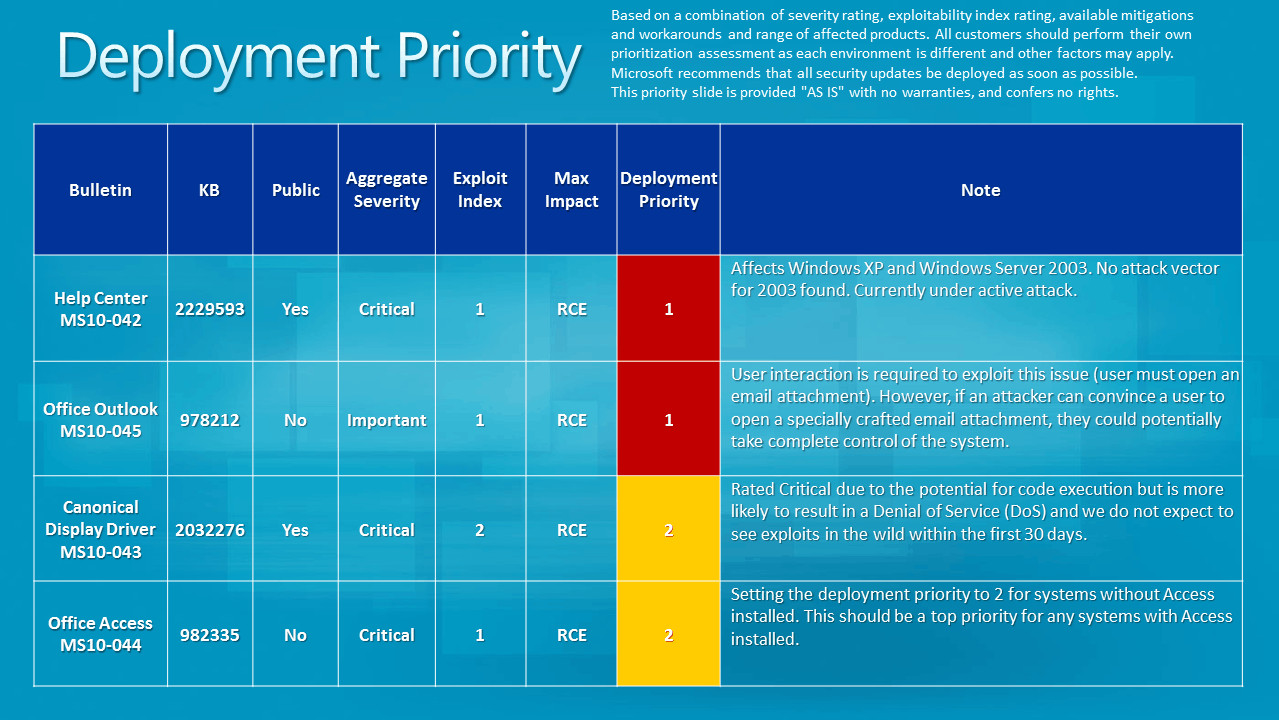
Here's a summary list:
- Adobe Flash Player
- Internet Explorer
- Microsoft Edge
- Microsoft Windows
- Microsoft Office and Microsoft Office Services and Web Apps
- ChakraCore
- ASP.NET
- Microsoft Exchange Server
- Team Foundation Server
- Azure DevOps Server
- Open Enclave SDK
- Windows Admin Center
Some updates correct issues so serious that, in certain situations, remote access to your computer may be possible without your permission. These issues are classified as critical, while most others are less serious and classified as important, moderate, or low.
See Microsoft Security Bulletin Severity Rating System for more on these classifications and the April 2019 Security Updates Release Notes for Microsoft's very brief summary on this collection of security updates.
Windows XP and Windows Vista are no longer supported by Microsoft and so no longer receive security patches. Windows Vista support ended on April 11, 2017 and Windows XP support ended on April 8, 2014.
In case you're curious: Windows 7 support ends on January 14, 2020 and Windows 8 support ends on January 10, 2023. Windows 10 support is slated to end on October 14, 2025, but expect that to be extended as future iterations of Windows 10 are released.
Are There Any Non-Security Updates This Patch Tuesday?
Yes, a number of non-security updates are being made available for all supported versions of Windows including, as usual, this month's update to the Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool.
Alabama Boat License Requirements. The minimum boating license age in Alabama is 12 years of age for motorized water vessels. No one under 12 years of age can independently operate a water vessel or PWC in Alabama. The requirements for drivers who are 12 or 13 years of age include being supervised at all times by a licensed boater over 21 years of age. Boat registrations are not pro-rated; the full registration fee will be charged regardless of when the registration is renewed. No refunds will be issued for registrations renewed prior to the designated 'renewal month.' Please be advised that the Alabama Law Enforcement Agency cannot be held responsible for lost or stolen decals. Boat/Vessel License Requirements Statewide licensing of boat operators began in all Alabama counties July 17, 1997 under the Boating Safety Reform Act. You must be at least 12 years of age to operate a motorized vessel on Alabama's waterways. Alabama boat license course. All persons who operate a motorized boat on Alabama waters need to obtain an Alabama Vessel License. You must be at least 12 years old to get your license. The Alabama vessel license is a required proof of boater education that must be included on your Alabama driver’s license if you would like to operate a boat or motorized vessel of any kind. This is sometimes called an “Alabama boating license.”.
Microsoft's Surface tablets also usually get driver and/or firmware updates on Patch Tuesday. You can get all the details on these updates from Microsoft's Surface Update History page. Individual update histories are available for of Microsoft's Surface devices.
There may also be non-security updates included this month for Microsoft software other than Windows. See the non-security update information in the section below for details.
Download Patch Tuesday Updates
In most situations, the best way to download patches on Patch Tuesday is via Windows Update. Only the updates you need will be listed and, unless you've configured Windows Update otherwise, will be downloaded and installed automatically.
See How Do I Install Windows Updates? if you're new to this or need some help.
You can usually find links to any non-security Microsoft Office updates on the Microsoft Office Updates blog.
Updates are typically not available to consumers for individual installation. When they are, or if you're a business or enterprise user, please know that most of these downloads come in a choice of 32-bit or 64-bit versions. See Do I Have 32-bit or 64-bit Windows? if you're not sure which downloads to choose.
Patch Tuesday Problems
While updates from Microsoft rarely result in widespread problems with Windows itself, they do frequently cause specific issues with software or drivers provided by other companies.
If you haven't yet installed these patches, please see How to Prevent Windows Updates From Crashing Your PC for a number of preventative measures you should take before applying these updates, including disabling fully automatic updates.
If you're having problems after Patch Tuesday, or during or after installing any Windows update:
- See How to Recover From a Frozen Windows Update Installation for help if your computer freezes during the installation of an update.
- See How to Fix Problems Caused by Windows Updates for help undoing the damage if the updates already installed but you're now experiencing a problem.
See Windows Updates & Patch Tuesday FAQ for answers to other common questions, including 'Does Microsoft test these updates before they push them out?' and 'Why hasn't Microsoft fixed the problem that their update caused on my computer?!'
Patch Tuesday & Windows 10
Microsoft has publicly commented that beginning with Windows 10, they will no longer be pushing updates solely on Patch Tuesday, instead pushing them more frequently, essentially ending the idea of Patch Tuesday altogether.
While this change goes for both security updates and non-security updates, and Microsoft is clearly updating Windows 10 outside of Patch Tuesday, so far they still seem to be pushing a majority of the updates to their latest operating system on Patch Tuesday.